What Makes Chipboard Screws a Superior Fastening Choice Today?
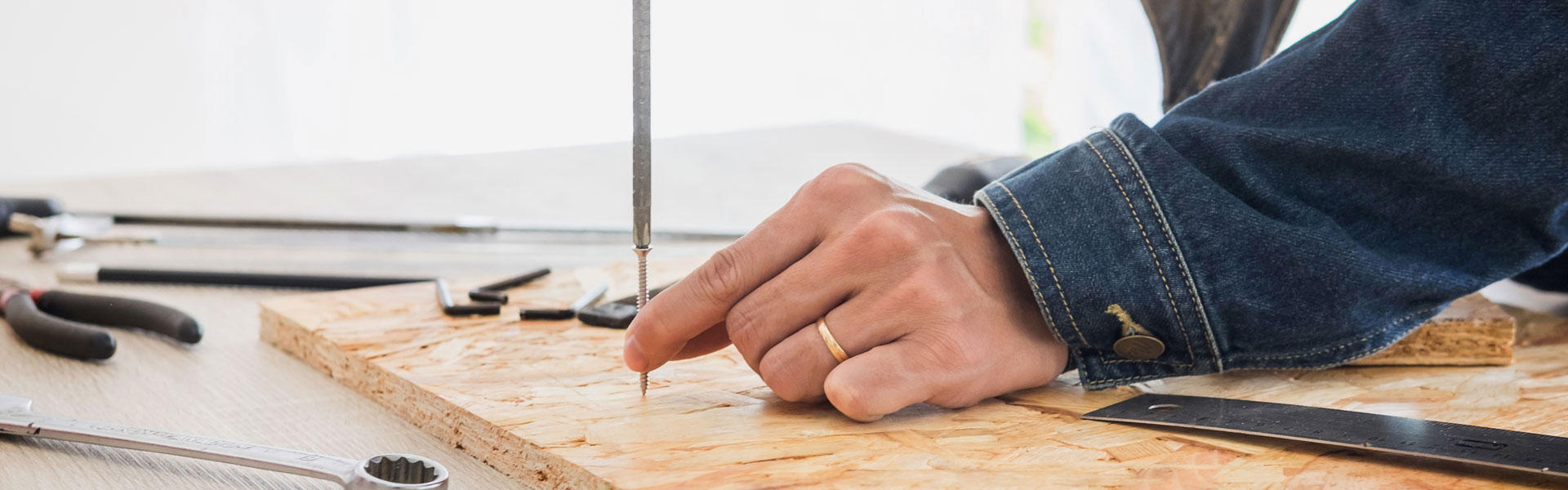
Chipboard screws have become one of the most widely used fastening components in modern construction, woodworking, and furniture manufacturing. Designed specifically for engineered wood substrates such as chipboard, MDF, particleboard, and laminated panels, these screws provide strong holding power, minimized splitting, and high installation efficiency. The growing need for stable and cost-effective materials in construction industries has put chipboard screws at the center of structural and decorative assembly work.
Understanding what makes chipboard screws effective requires examining their unique thread structure, tip geometry, and material hardness. Chipboard screws typically feature deep, coarse threads that maximize grip in low-density materials. Their sharp tips allow quick penetration without requiring pre-drilling in most cases, offering reduced labor time and improved workflow consistency. The main objective of this article is to explore the advantages, functions, usability, and future trends of chipboard screws while presenting clear product data and practical industry insights.
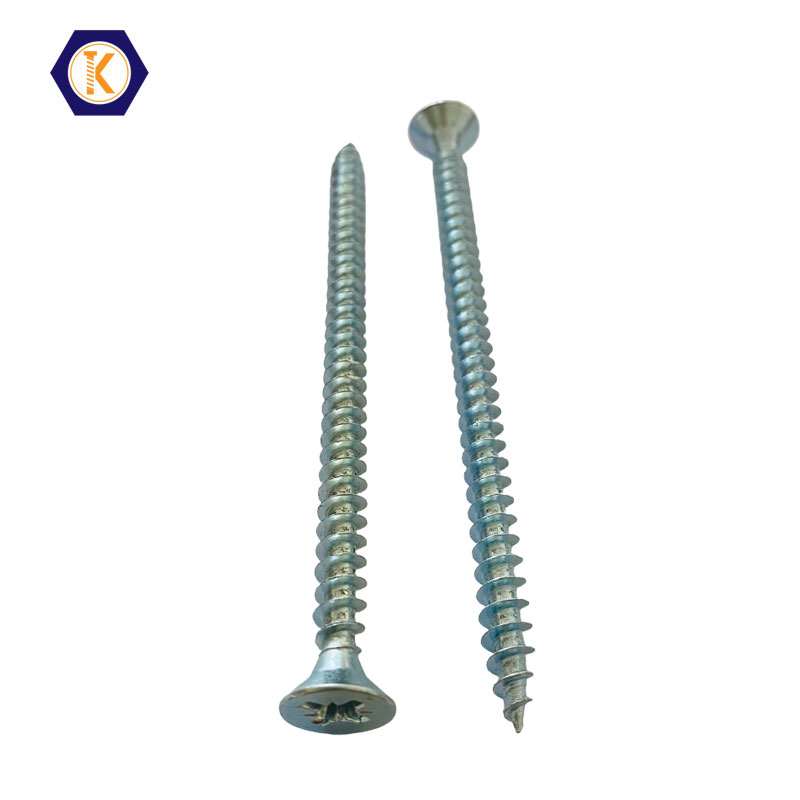
Product Parameters of Chipboard Screws
| Parameter | Specification Description |
|---|---|
| Material Options | Carbon Steel, Stainless Steel (304/316), Alloy Steel |
| Surface Treatments | Zinc Plating, Yellow Zinc, Black Phosphate, Nickel, Ruspert Coating |
| Head Types | Countersunk, Pan Head, Wafer Head, Bugle Head |
| Drive Types | Phillips, Pozidriv, Torx/Star Drive |
| Thread Types | Coarse Single Thread, Double Thread, Twinfast Design |
| Tip Options | Sharp Point, Drill Point, Type-17 Cutting Point |
| Size Range | Diameter: 3.0mm–6.0mm; Length: 12mm–200mm |
| Applications | Woodworking, Furniture Assembly, Cabinetry, Panel Fixing, Construction |
Chipboard screws are specifically engineered to strengthen structural connections in wooden and composite materials. Their specialized geometry distributes stress evenly, preventing pull-out, cracking, and loose anchoring—issues often seen with generic wood screws. Their role continues to expand as eco-friendly engineered wood boards replace solid hardwood in global manufacturing.
Why Are Chipboard Screws Engineered Differently and Why Do Industries Rely on Them?
To understand why chipboard screws stand out, it is necessary to analyze the engineering requirements of chipboard and other composite wood materials. Chipboard has a lower density and less grain strength compared to natural lumber. As a result, fastening methods must provide maximum surface contact and thread engagement.
Why Do Chipboard Screws Have Deep, Coarse Threads?
Deep and widely spaced threads increase frictional grip in soft or loose-fiber materials. Compared with fine threads used in metal screws, chipboard screw threads displace fibers more efficiently, allowing the screw to anchor securely. This ensures superior holding power and reduces the risk of stripping during installation.
Why Does the Tip Design Matter?
The tip of a chipboard screw determines how smoothly it penetrates board materials. Sharp tips and type-17 cutting points reduce the need for pre-drilling by slicing through fibers cleanly, which prevents splitting near edges and corners. This feature significantly improves installation speed and reduces labor costs.
Why Is Surface Treatment Essential for Durability?
Surface treatments affect corrosion resistance, lubricity, and driving stability. Yellow zinc and ruspert coatings improve rust protection in humid or coastal environments, while black phosphate enhances torque control and reduces friction during installation. These factors make chipboard screws suitable for both indoor and semi-exposed applications.
Why Do Industries Prefer Chipboard Screws in Mass Production?
Large furniture, cabinetry, and construction manufacturers rely on chipboard screws because they deliver:
-
Consistent torque performance for automated driving machines
-
Reliable structural stability in engineered wood boards
-
Reduced production errors due to anti-split features
-
Faster assembly time with no pre-drilling
-
Lower overall material and labor costs
This combination allows manufacturers to maintain efficiency and product quality while minimizing waste.
Chipboard screws also support modern design trends, which increasingly favor modular assembly, flat-pack furniture, reusable hardware, and eco-friendly engineered wood boards. In these systems, screws must provide strength while enabling easy disassembly when needed.
How Do Chipboard Screws Perform in Practical Applications and How Should They Be Selected?
Chipboard screws are versatile, but selecting the correct type ensures optimal structural performance. Their effectiveness depends on matching screw characteristics with specific materials and load requirements.
How Do Chipboard Screws Provide Holding Power in Wood Composites?
Chipboard screws compress and grip wood particles as the threads rotate, forming a tight bond that resists vertical pull-out and horizontal shear forces. Unlike standard wood screws that may loosen over time in softer materials, chipboard screws maintain long-term stability due to:
-
Enhanced thread geometry
-
Higher torque resistance
-
Longer thread lengths
-
Superior stress distribution
These features make them suitable for load-bearing applications such as cabinetry frameworks, shelving supports, and indoor construction panels.
How Should Screw Length and Diameter Be Chosen?
Choosing the correct size ensures proper anchoring depth and prevents board damage:
-
Longer screws are preferred for structural panels, frameworks, and joint reinforcements.
-
Shorter screws fit thin laminates, drawer sides, and lightweight components.
-
Thicker diameters increase holding power but require proper spacing to avoid splitting.
-
Smaller diameters work well for delicate components or edge fastening.
A general guideline is that the screw should penetrate at least two-thirds of the thickness of the receiving material for maximum strength.
How Do Different Drive Types Affect Installation Efficiency?
-
Torx/Star drive: Best for automated assembly, high torque, minimal cam-out
-
Pozidriv: Balanced torque and control for general woodworking
-
Phillips: Universally compatible but prone to cam-out under heavy load
Manufacturers using high-speed electric drivers typically choose Torx for its stability and precision.
How Does Coating Selection Improve Performance?
-
Yellow zinc: Ideal for indoor furniture and general carpentry
-
Black phosphate: Reduces friction and is suited for hidden joints
-
Nickel: Suitable for decorative fixtures requiring a polished appearance
-
Ruspert: Best for high-corrosion environments such as bathrooms or semi-outdoor areas
Correct coating selection increases product lifespan and customer satisfaction.
How Do Chipboard Screws Support Modern Construction Trends?
Chipboard screws align with several growing industry trends:
-
Eco-friendly materials: As engineered boards replace solid wood, these screws ensure structural reliability.
-
Modular and prefabricated construction: Quick installation supports mass-production workflows.
-
Flat-pack furniture: Strong grip yet easy disassembly enhances convenience.
-
Automation in manufacturing: Consistent torque response suits robotic assembly tools.
-
Lightweight interior design: Their high pull-out resistance allows thinner materials to be used safely.
These factors position chipboard screws as essential components in the evolution of contemporary construction and furniture manufacturing.
What Are the Future Trends of Chipboard Screws and How Will Innovation Shape Their Development?
The continuing global shift toward sustainable materials, modular building systems, and intelligent manufacturing technologies will influence the future development of chipboard screws. Several trends are becoming increasingly evident across industries.
What Future Innovations Are Expected in Chipboard Screw Design?
-
Advanced Anti-Corrosion Technology
Coating technologies are expected to evolve, offering longer protection in moisture-rich environments while remaining cost-effective. Multi-layer ceramic treatments and eco-friendly rust-barrier coatings are increasingly popular. -
Higher-Precision Thread Engineering
Improved cutting geometries may increase torque efficiency and reduce installation time, benefiting automated assembly lines. -
Sustainable Materials
Manufacturers are developing screws made from recycled metals or environmentally optimized steel alloys to support global sustainability goals. -
Integration With Smart Manufacturing
As factories embrace automated production, screws designed for consistent robotic driving will become standard. Enhanced drive recesses and self-centering features will support automation.
How Will Chipboard Screws Support the Future of Engineered Wood?
Engineered wood panels continue to evolve, offering higher density, better moisture resistance, and more stable fiber structures. Chipboard screws must adapt to these materials with:
-
Stronger thread profiles
-
Coatings optimized for moisture-resistant boards
-
Improved compatibility with laminated and fire-retardant surfaces
This ensures that the screws maintain their role as reliable connectors in increasingly advanced substrates.
How Will Global Manufacturing Standards Influence Product Quality?
Demand for standardized production quality will increase as companies expand globally. Screws must comply with:
-
International torque and tensile requirements
-
Quality inspection systems for mass production
-
Consistent surface treatment performance
-
Material traceability for sustainability reporting
Manufacturers that adopt strict quality control will be better positioned to meet the rising expectations of global buyers.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What makes chipboard screws different from regular wood screws?
A1: Chipboard screws have deeper, coarser threads specifically designed for low-density materials like chipboard and MDF. These threads provide stronger grip and prevent stripping, which commonly occurs when using standard wood screws in engineered materials.
Q2: How can chipboard screws prevent splitting during installation?
A2: Most chipboard screws include a sharp tip or type-17 cutting point that pierces wood fibers cleanly. This prevents outward pressure buildup along the board edges, reducing splitting even when driving into thin or delicate materials.
Q3: What type of coating should be used for areas with high humidity?
A3: Ruspert and yellow zinc coatings offer excellent corrosion resistance in moisture-rich environments. They protect the screw surface from rust while maintaining structural strength, making them suitable for kitchens, bathrooms, and semi-outdoor installations.
Why Chipboard Screws Will Remain a Key Component in Wood-Based Construction
Chipboard screws continue to be essential in woodworking, construction, furniture production, and interior design due to their strong holding power, installation efficiency, and compatibility with engineered wood materials. Their specialized thread geometry, advanced coatings, and growing alignment with automation make them a reliable and future-ready fastening solution. As manufacturing technologies evolve, demand for high-quality chipboard screws will remain solid across global industries.
For businesses seeking durable and precisely engineered fastening products, Zhejiang Kangying Hardware Technology Co., Ltd. offers a comprehensive range of chipboard screws engineered for long-term performance and consistent quality.
To learn more or request product specifications, contact us for detailed assistance and professional support.